 Jan, 13 2026
Jan, 13 2026
Every pill you take should work exactly as it should. No more, no less. But what happens when a fake version slips into the supply chain? Counterfeit drugs don’t just fail to help-they can kill. In 2022, Interpol seized over $21 million worth of fake medicines, and 78% of them were falsely labeled as generic drugs. The truth? Most of these fakes wouldn’t even pass a basic lab test-if they were tested at all. But in countries with strong regulations, the system is built to stop them before they ever reach you.
Why Generic Drugs Are Held to the Same Standard as Brand-Name Drugs
Many people think generic drugs are cheaper because they’re less regulated. That’s false. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires every generic drug to meet the same exact standards as the brand-name version. It’s not about cost-it’s about control. The law doesn’t allow a generic manufacturer to say, “It’s close enough.” It has to prove it’s identical in active ingredient, strength, dosage form, and how it works in the body. This is enforced through the Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) process. To get approval, a generic maker must show bioequivalence: the drug releases into the bloodstream at the same rate and amount as the original. The acceptable range? 80-125% of the brand’s performance. That’s tighter than most people realize. In some countries, the range is wider-75-133%-which is why fake drugs often flood markets with weak oversight. The FDA doesn’t just review paperwork. They inspect manufacturing sites. In 2023, U.S.-based generic facilities had a 94% compliance rate with cGMP rules. Facilities in India and China? Those numbers dropped to 78% and 65%. That’s not a coincidence. It’s a warning.What cGMP Really Means: Quality Can’t Be Tested In
You can’t inspect quality into a pill. That’s the core idea behind Current Good Manufacturing Practices, or cGMP. It’s not a checklist. It’s a mindset. The FDA says it plainly: “Quality must be built into every step.” That means:- Every raw material is tested against a reference standard before it’s used.
- Production happens in clean rooms with air so clean it has fewer than 3,520 particles per cubic meter (ISO Class 5).
- Every batch is tracked with electronic records-no handwritten logs.
- Environmental conditions like humidity and temperature are monitored in real time.
- Equipment is cleaned and validated to prevent cross-contamination.
The Digital Shield: Serialization and Track-and-Trace
In 2023, 92% of the top 50 generic manufacturers used serialization-each pill bottle or blister pack has a unique barcode or QR code. It’s like a digital fingerprint. When you scan it, you can trace the drug back to the factory, the batch, and even the exact machine that made it. This isn’t just for show. Under the U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act, every package must be verifiable by pharmacies and distributors. If a bottle shows up without a valid code, it’s flagged. If the code doesn’t match the manufacturer’s database, it’s pulled. The system is 99.99% accurate. And it’s forced counterfeiters to change tactics. No longer can they just print fake labels. They now need to replicate the digital chain-something that requires hacking into secure systems, forging encryption keys, and bypassing global databases. Most can’t. And those who try? They get caught.
What Gets Missed: Polymorphs and Hidden Impurities
Even the best systems have blind spots. In 2018, a generic version of the blood thinner valsartan was recalled because of a cancer-causing impurity. The drug passed all standard identity and potency tests. But the problem? The molecule had the wrong crystal structure-a polymorph-that changed how it broke down in the body. Standard tests didn’t catch it. This isn’t rare. Some counterfeiters now replicate the chemical formula perfectly but alter the physical form to cut costs. The result? A pill that looks right, tests right, but doesn’t work right. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has a stronger safeguard: the Qualified Person (QP) system. Before any batch leaves the factory, a certified expert must personally sign off on it. The U.S. system relies more on process validation-proving the entire system works over time. Both work, but the QP system adds a human layer of accountability that’s harder to fake.Why eQMS and AI Are Changing the Game
Most generic drug makers now use Electronic Quality Management Systems (eQMS). These aren’t just databases. They’re live dashboards that track over 15,000 quality parameters per batch. If a temperature spike happens during drying, or a mixing time goes off by 0.5 seconds, the system flags it immediately. By 2023, 78% of major manufacturers had moved to cloud-based eQMS platforms. Companies like Veeva QualityOne are now using AI to analyze spectral data from 50+ different angles to spot fake ingredients. One lab manager at Teva told a Reddit forum that after implementing their system, deviation resolution time dropped from 14 days to 48 hours. But it’s expensive. Installing a full eQMS costs $2-5 million. The spectrometers alone run $500,000-$1 million. That’s why smaller manufacturers lag behind. And that’s where the risk lives.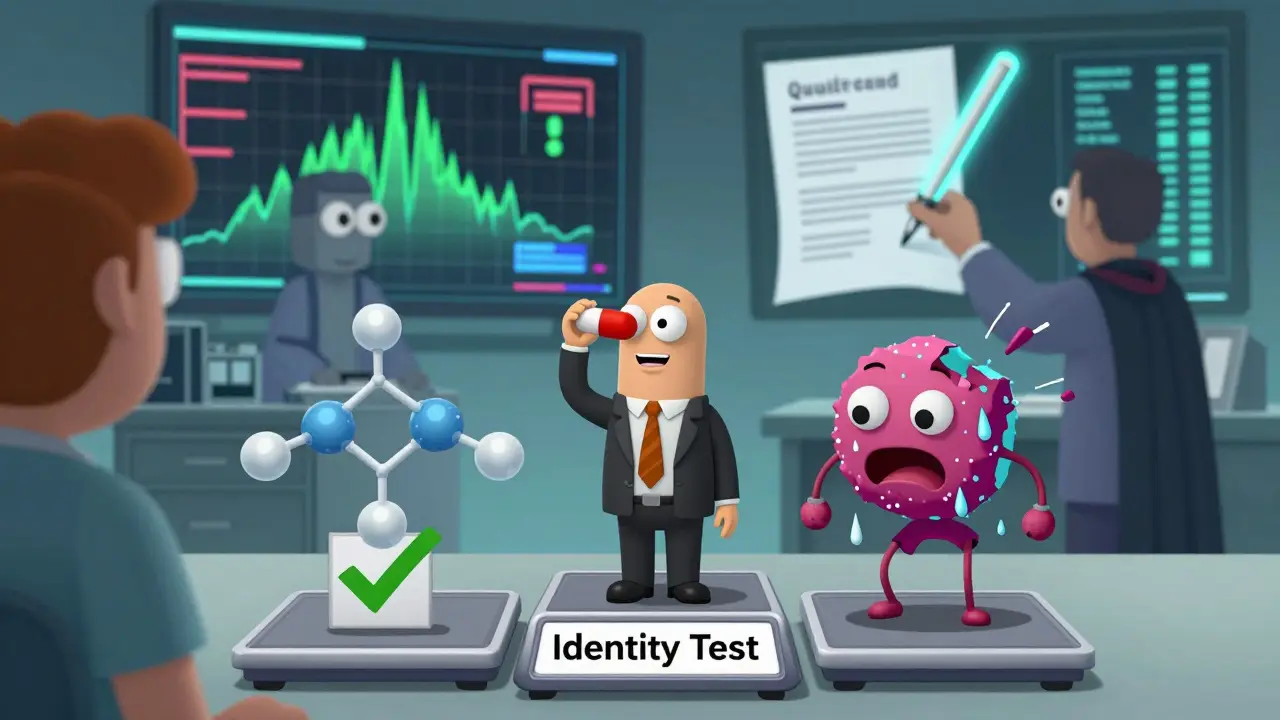
What Happens When Standards Break Down
The global generic drug market is worth $462 billion-and growing fast. But in countries with weak regulation, up to 30% of medicines are fake. The WHO says counterfeit drugs cause over 100,000 deaths annually in Africa and Southeast Asia alone. In the U.S., the rate is under 0.1%. Why? Because of enforcement. The FDA doesn’t just inspect factories. They audit suppliers, test products bought off the street, and shut down illegal online pharmacies. In one 2023 operation, they seized over 1.2 million fake pills-mostly labeled as generics for diabetes, high blood pressure, and erectile dysfunction. Meanwhile, over-the-counter supplements? They’re under a different law (DSHEA). Only 30% of supplement makers test for identity. That’s why fake vitamins and “herbal” weight-loss pills are so common. But prescription generics? They’re held to a different standard. And that difference saves lives.The Future: Quantum Codes and Molecular Taggants
The next wave of defense is invisible. Researchers are testing molecular taggants-tiny chemical markers added to pills that can’t be copied without the original formula. These taggants can be detected with handheld scanners, even in remote areas. The EU is already requiring quantum-resistant encryption for drug codes by 2026. Why? Because future hackers could use quantum computers to break current barcodes. The industry is preparing now. And AI is getting smarter. IBM and Siemens have invested $1.2 billion in AI tools that predict manufacturing flaws before they happen. By 2027, these systems could reduce counterfeit incidents by 40%. But the biggest threat isn’t technology-it’s complacency. When a country cuts corners on inspections, when a lab skips a test to save time, when a distributor ignores a mismatched code-that’s when fakes get through.What You Can Do
As a patient, you can’t test a pill in your kitchen. But you can ask questions:- Where was this drug made?
- Is the pharmacy licensed?
- Does the packaging look right? (Faded print, misspellings, odd colors?)
- Did the pill look different from your last refill?
Are generic drugs as safe as brand-name drugs?
Yes-when they’re made under proper quality control. The FDA requires generic drugs to have the same active ingredient, strength, dosage form, and bioequivalence as the brand-name version. Studies show the adverse event rate for FDA-approved generics is 0.02%, compared to 0.03% for brand-name drugs. The difference is negligible. What matters is whether the manufacturer follows cGMP standards.
Can I tell if a generic drug is fake just by looking at it?
Sometimes, but not always. Fake pills might have blurry printing, wrong colors, or misspellings. But sophisticated counterfeits look identical. The only reliable way to confirm authenticity is through digital track-and-trace systems or lab testing. Never rely on appearance alone.
Why are counterfeit drugs more common in some countries?
Countries with weak regulatory agencies, poor inspection systems, and limited enforcement struggle to stop counterfeits. In places where inspectors are underfunded or corrupt, fake drugs enter the supply chain easily. The WHO estimates counterfeit rates of 10-30% in regions with weak oversight, compared to under 0.1% in countries with strong systems like the U.S., EU, Canada, and Australia.
Do all generic drug manufacturers follow the same rules?
All FDA-approved manufacturers must follow cGMP, regardless of location. But inspections are more frequent and rigorous in the U.S. than in some other countries. Facilities in India and China have lower compliance rates (78% and 65%, respectively), meaning more risk. Always check where your drug is made and whether the manufacturer is FDA-registered.
How do I know if my pharmacy is selling legitimate generics?
Use only licensed, in-person pharmacies or verified online pharmacies (those with VIPPS certification in the U.S.). Avoid websites that sell drugs without a prescription, offer “miracle cures,” or have prices far below market rate. If you’re unsure, ask your pharmacist where the drug comes from. Reputable pharmacies can provide manufacturer details and batch numbers.

Henry Sy
January 14, 2026 AT 11:07So let me get this straight-we’re supposed to trust pills made in some factory in India where the air smells like regret and the inspectors get paid in chai? I’ve seen more quality control in my cat’s litter box.
Sarah Triphahn
January 15, 2026 AT 00:53Let’s be real. The FDA doesn’t care about you. They care about liability. That 94% compliance rate? It’s because they only inspect the ones they already know are sketchy. The rest? They assume it’s fine until someone dies. Then they issue a press release.
Vicky Zhang
January 15, 2026 AT 10:01I just want to say how amazing it is that we have systems in place that actually protect us. I mean, think about it-someone, somewhere, is checking the humidity in a room so a pill can dissolve properly in your stomach. That’s science. That’s care. That’s the quiet heroes we never thank.
My grandma takes generics for her blood pressure. She doesn’t know about cGMP or spectroscopy. But she’s alive because someone cared enough to make sure her pill wasn’t sugar with a sticker.
We should be proud. Not scared. This system works. It’s not perfect, but it’s the best we’ve got.
Allison Deming
January 16, 2026 AT 11:27It’s ironic that we praise the FDA’s rigor while ignoring the fact that most people can’t afford brand-name drugs. The system is designed to protect the wealthy who can demand traceability and transparency. The rest of us? We’re just hoping the pill we bought off Amazon isn’t a placebo with a side of arsenic.
Quality control is a privilege, not a right. And that’s the real scandal here.
Susie Deer
January 18, 2026 AT 08:17USA best. Rest of world is a dumpster fire. End of story.
Andrew Freeman
January 19, 2026 AT 16:10you know what’s wild? the fda inspects like 5% of factories. the rest is paperwork and prayers. if you think this system is airtight you’ve never seen a batch log from a 3rd world plant
says haze
January 21, 2026 AT 04:59What we’re really celebrating here is not safety-it’s capitalism’s ability to outsource risk. The U.S. outsources manufacturing, then outsources accountability to a regulatory body that’s underfunded and politically neutered. The fact that 78% of Indian facilities comply? That’s not a triumph. It’s a low bar.
And don’t get me started on AI. You think a machine can detect a polymorph? It can detect patterns. It can’t understand why someone chose to cut corners because the wage is $2 a day and the CEO made $12 million last year.
This isn’t science. It’s theater. And we’re all paying for front-row seats.
Anna Hunger
January 22, 2026 AT 20:43The rigor of the FDA’s ANDA process is one of the most scientifically sound regulatory frameworks in the world. Bioequivalence thresholds of 80–125% are not arbitrary-they are based on decades of pharmacokinetic data and clinical outcomes. The requirement for identical active pharmaceutical ingredients, dosage forms, and dissolution profiles ensures therapeutic interchangeability.
Furthermore, cGMP compliance is not a suggestion; it is legally enforceable. Facilities are subject to unannounced inspections, and violations can result in import alerts, consent decrees, or criminal prosecution. The 94% compliance rate reflects a culture of accountability, not luck.
Serialization and track-and-trace systems under DSCSA are not merely technological upgrades-they are structural safeguards against supply chain fragmentation. Each unique identifier enables real-time verification, reducing the likelihood of falsified products entering the distribution chain.
While emerging threats like polymorphs and molecular tampering require continuous innovation, the foundational framework remains robust. The challenge lies not in the system’s design, but in global enforcement equity.
It is misleading to imply that regulatory divergence in other countries reflects inherent inferiority. Rather, it reflects disparities in institutional capacity, investment, and political will. The U.S. model is replicable-but requires sustained commitment.
Patients deserve confidence. The system delivers it-when properly resourced and uniformly applied.
shiv singh
January 23, 2026 AT 17:46Oh wow, so America is perfect? Tell that to the 200,000 people who died from opioids because Big Pharma bribed doctors and the FDA looked away. You think generics are the only problem? The whole system is rigged. The FDA is a revolving door for pharma execs. You think they care about you? They care about their next job at Pfizer.
And don’t even get me started on how they let Chinese factories get certified while ignoring real safety issues. You’re drinking the Kool-Aid and calling it science.
TooAfraid ToSay
January 25, 2026 AT 04:00So you’re telling me the only reason generics are safe in the US is because we’re rich enough to pay for inspections? What about the rest of the world? Are we supposed to just accept that millions die because they’re poor? That’s not science. That’s colonialism with a pill bottle.
Dylan Livingston
January 27, 2026 AT 03:01Oh please. You think AI is going to save us? The same AI that got fooled by deepfake pills last year? The same AI that flagged a legitimate batch because the humidity sensor glitched? This isn’t progress-it’s overconfidence dressed in code.
And don’t even mention quantum encryption. You think a hacker in Belarus can’t just bribe a lab tech to hand over the key? The real vulnerability isn’t the barcode-it’s the human.
Every time someone says ‘the system works,’ they’re ignoring the fact that the system is designed to protect profits, not patients.
Alvin Bregman
January 28, 2026 AT 04:19im just glad we have any system at all. my cousin in nairobi got a fake malaria pill last year. it was just cornstarch with red dye. he lived. but not everyone does. the fact that we can even talk about spectroscopy and polymorphs means we’re ahead of most of the world. not perfect. but better than nothing.
Robert Way
January 29, 2026 AT 12:16wait so if a pill has the right chem but the wrong crystal shape its still fake but the test says its good? so the tests are useless? why do we even bother?
Sarah -Jane Vincent
January 29, 2026 AT 14:34They’re lying. The FDA doesn’t test 99.9% of generics. They rely on manufacturers’ self-reporting. The whole track-and-trace system? It’s a scam. The barcodes can be cloned. The encryption? Broken in 2021 by a grad student in Ukraine. They just don’t tell you because they’re scared people will panic. The real danger? It’s not the pills-it’s the silence.